Sistemas de Arquivos Distribuídos
Leitura
- Sistemas Distribuídos: princípios e paradigmas, 2a edição. Capítulo 11: Sistemas de Arquivos Distribuídos.
- Distributed Systems: Concepts and Designs. Capítulo 12: Distributed File Systems.
Google File System
- Google, 2003
- File System
- Dados recuperados da Internet usados em consultas
- Milhões de arquivos de múltiplos GB
- Chunks de 64MB (``blocos do disco'')
- Operações comuns são appends ou reads
- Servidores/discos/memórias estão sempre falhando
- Centenas de clientes concorrentes no mesmo arquivo

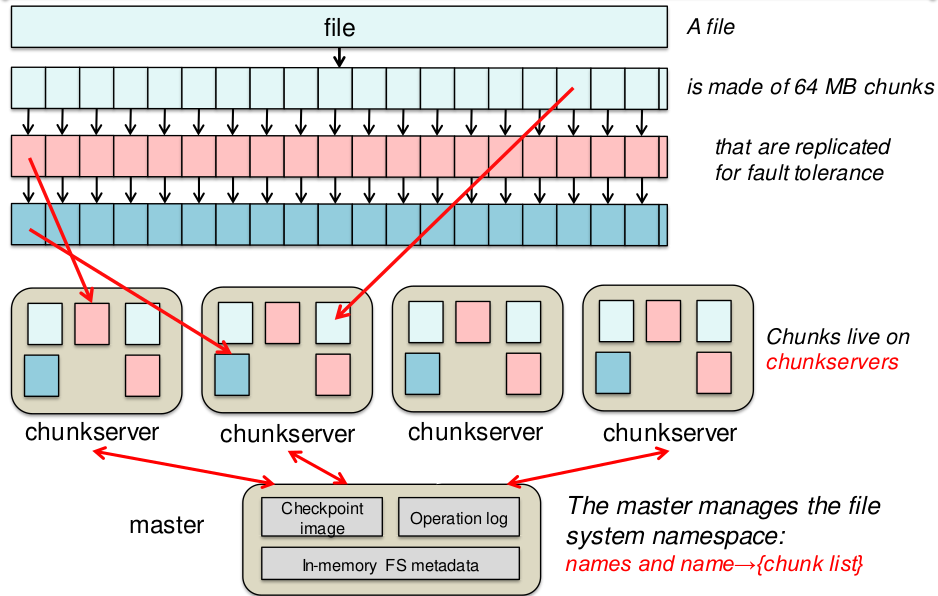
- Clusters de nós ``comuns''
- Master node: metadata
- Chunk servers: data
- Permite usar um cluster como um único HD elástico na rede.

- Apps recebem leases de acesso direto aos dados
- Atomic commitment garante consistência entre réplicas
-
Consistência
-
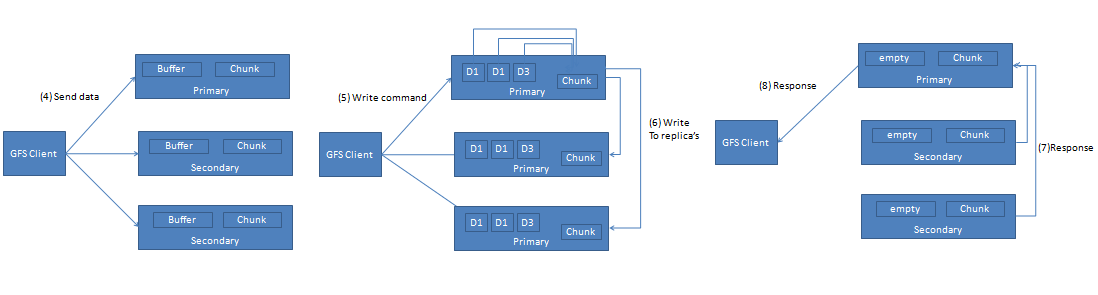
Application sends the file name and data to the GFS client.
- GFS Client send the file name and chunk index to master
- Master sends the identity of the primary and other secondary replicas to the client.
- Client caches this information. Client contacts master again only when primary is unreachable or it sends a reply saying it does not holds the lease anymore.
- Considering the network topology the client sends the data to all the replicas.This improves performance. GFS separates data flow from the control flow. Replicas store the data in their LRU buffers till it is used.
- After all replicas receiving of the data, client sends write request to the primary. Primary decides the mutation order. It applies this order to its local copy.
- Primary sends the write request to all the secondary replicas. They perform write according to serial order decided by the primary.
- After completing the operation all secondary acknowledge primary.
- Primary replies the client about completion of the operation. In case of the errors that is when some of the secondary fail to write client request is supposed to be fail.This leaves modified chunk inconsistent.
- Client handles this by retrying the failed mutation.